What Is An MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging, technically called MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), is a non-invasive technology that produces three-dimensional anatomical images. Through this methodology, it is intended to obtain information from certain parts of the body.
MRIs prevent the use of radiation that can be harmful. Instead, they use powerful radio waves and magnets to create images of the body.
Its operation is based on an effective technique. It consists of stimulating and detecting the change in the direction of the axis of rotation of the protons of the hydrogen atoms. The images produced through this are called slices and are generally stored on computers, although they can also be printed on film.
In a single examination performed with an MRI, tens to hundreds of images can be produced.
How do MRIs work?
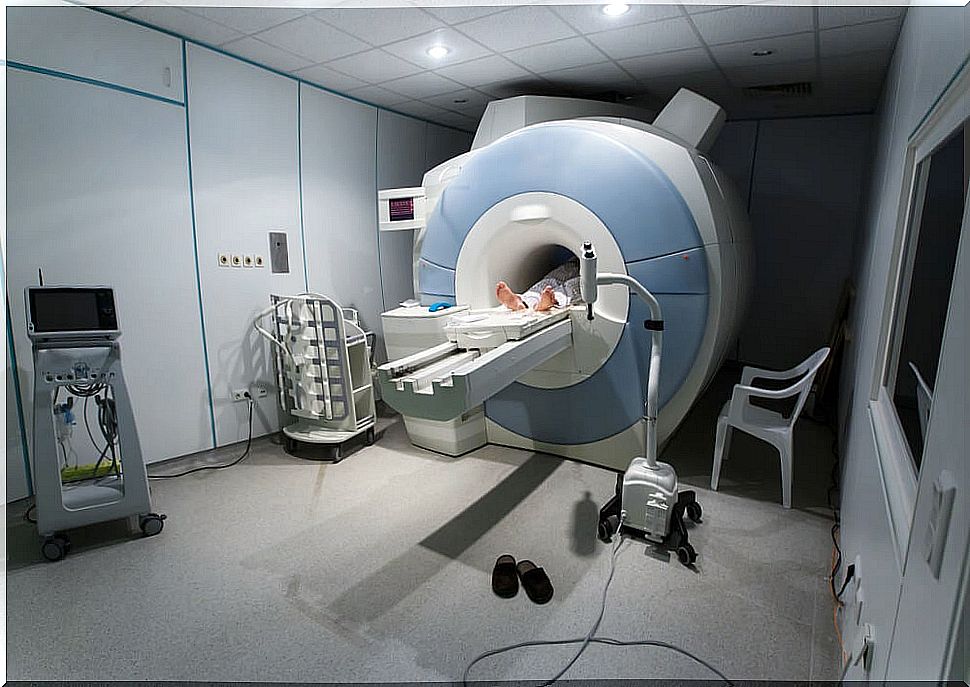
MRIs use powerful magnets to function. Its main function is to produce a large magnetic field. This field forces the protons in the body to align themselves. By pulsing a radio frequency current through the patient, the protons are stimulated and spin out of balance, fighting against this magnetic force.
Subsequently, by turning off the radio frequency field, the MRI sensors are able to detect the released energy. The protons then realign with the magnetic field. The amount of energy released, as well as the time it takes for protons to realign with the magnetic field, changes depending on the chemical nature of the molecules.
Professionals have the ability to identify the difference between different types of fabrics based on the magnetic properties mentioned.
What is MRI used for?
Typically, MRIs are used for disease detection and diagnosis and treatment monitoring. They are especially suitable for imaging non-bony or soft tissue parts of the body.
As mentioned above, they do not use the harmful ionizing radiation from other technologies, such as CT (computed tomography) or X-rays. Also, the muscles, ligaments and tendons, as well as the brain, nerves and muscles. spinal cord, are seen more clearly through MRI than with other methodologies.
It is for this reason that they are also frequently used to detect shoulder or knee injuries. Specifically, in the case of the brain, MRIs can be used to:
- Detect tumors.
- Diagnose aneurysms.
- Differentiate between white matter and gray matter.
Thanks to the fact that MRIs do not use radiation, it is an especially favorable method when frequent images are required for different diagnoses or therapies when it comes to the brain.
It should be mentioned that there is a class of specialized MRI, called functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).
This is used to observe the structures of the brain and determine which areas of the brain consume the most oxygen and are activated during cognitive tasks. Above all, through this technology, we want to promote the understanding of the organization of the brain. F IMR has great potential to assess neurological status and neurosurgical risk.
How is the MRI performed?

First, when you want to perform an MRI, the specialists ask the patient to wear garments without metal clasps. The reason is that d eterminados types of metal can cause blurred images.
For the development of magnetic resonance, in many cases, the use of a special dye as a contrast medium is required. This dye is administered intravenously through the hand or forearm before the exam. This contrast medium will help the specialist to see certain areas more clearly.
In addition, small devices, called spirals, can also be placed around the different areas to be studied. With the use of these devices, the quality of the images can be improved because they help to send and receive radio waves.
Finally, the MRI lasts approximately 30 to 60 minutes, although in certain circumstances it can increase that time.
What risks can they imply?
MRIs do not emit harmful radiation, but they do use a powerful magnetic field. This involves certain risks:
- The magnetic field created exerts very powerful forces on iron objects (extending even beyond the machine). Implant patients should notify their physician of this fact prior to the scan.
- Loud noise. In certain MRIs, sound intensity of up to 120 decibels may require special hearing protection.
- Many patients with anxiety or claustrophobia can have their mental health compromised. This usually happens during the test. Some people feel very overwhelmed from being inside the machine and experience rapid heartbeats and even panic attacks.
Should we be afraid of it?

In the aforementioned cases, it is important to explain that there is no type of physical risk to the person. Those who undergo an MRI have already been evaluated by their doctor and followed his instructions, so there is nothing to fear.
In the same way, it is important to realize that it is a technique that lasts for a short period of time. It is advisable to try to establish breathing exercises when nervousness appears and think that it is something necessary.